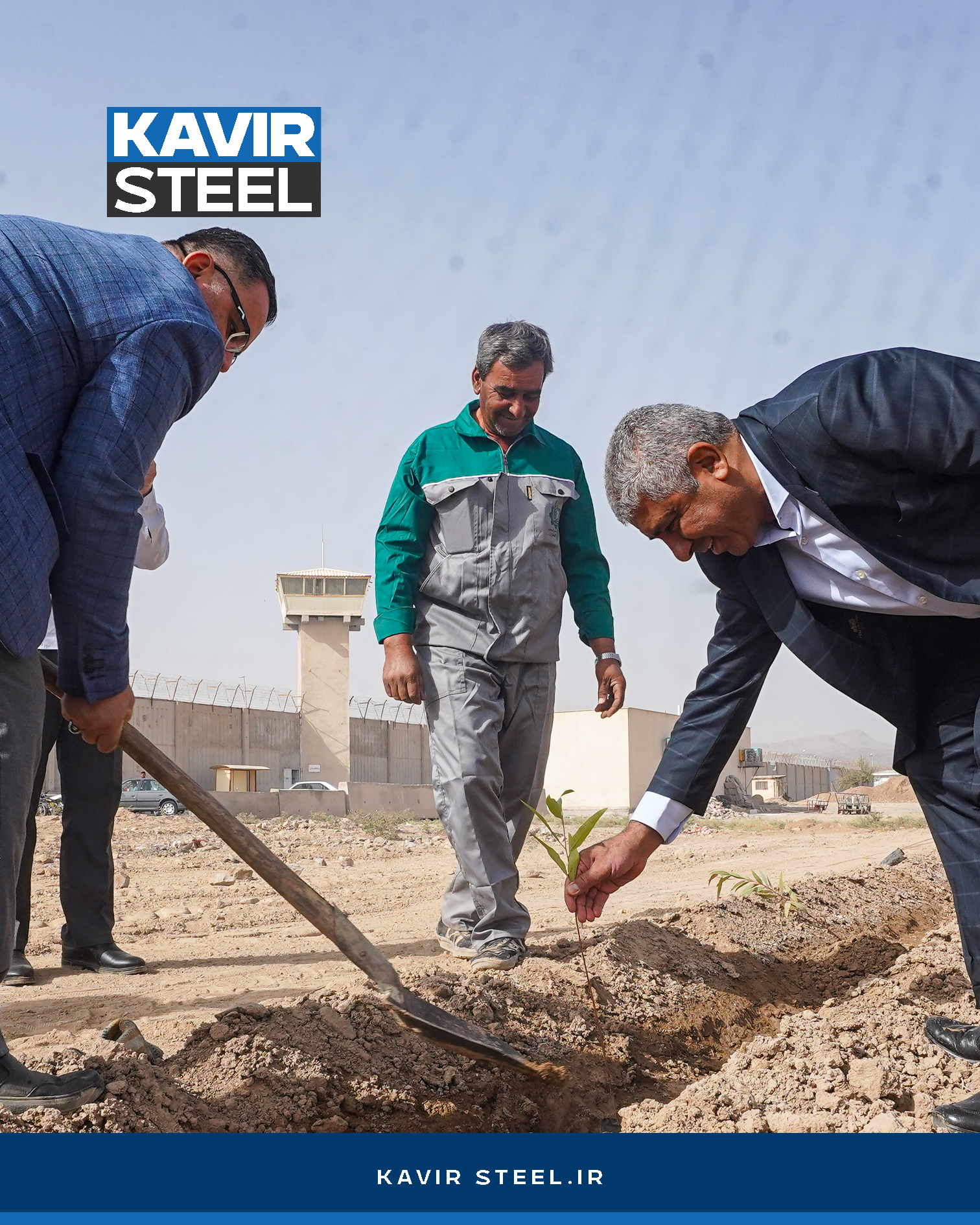
Tree-planting program at Kashan Prison
Kavir Steel’s Social Responsibility: Safeguarding Water, Air, and the Future
Advancing on the Foundation of Global StandardsKavir Steel’s Social Responsibility: Safeguarding Water, Air, and the Future
The concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) emerged in the early twentieth century with the rapid growth of industries. By the 1960s and 1970s, CSR had formally entered business structures as a key performance indicator. In Iran, the modern understanding of CSR began to take shape in the 2000s, leading to the expansion of related initiatives.
However, in Iran this concept has often drifted away from its true meaning. The core of this misalignment stems from a fundamental misconception: many companies assume that a few charitable or promotional projects are sufficient to fulfill their social responsibility. In reality, genuine CSR demands a fundamental transformation in the way a business is managed—modifying behavior so that, in addition to economic value, the company creates benefits for society and public well-being.
Kavir Steel, with a clear understanding of CSR principles, has taken meaningful steps toward reforming and improving its production processes. In line with responsible water management in its current production lines and air protection in its development projects, the company has implemented bold, thoughtful, and voluntary initiatives that have led to the creation of transformative, large-scale projects in Iran’s steel industry.
A few years after commencing operations in 2007, Kavir Steel developed water-recycling and brackish-water desalination systems that dramatically reduced water consumption. Nevertheless, in 2016, following extensive studies and a major strategic decision, the company fully eliminated its dependence on groundwater resources by establishing an advanced wastewater treatment facility. Today, the plant supplies its required water through the treatment of municipal wastewater. Owing to the high level of technology used and the exceptional quality of the output, the rolling-mill water-recycling system—with three times the previous capacity—successfully reduced water consumption to one-third.
In addition, for the steelmaking project, Kavir Steel is implementing a highly modern water-supply system based on a closed-loop circuit, which will significantly reduce water usage in the steelmaking process. On the environmental front, the project also incorporates a state-of-the-art Fume Extraction System (FES), equipped with the latest global technologies, which reduces emission levels to more than 16 times below environmental standards.
CSR is not limited to financial contributions—it must be integrated into the core structure and long-term strategies of companies. The reality is that Corporate Social Responsibility must be a sustained, systemic commitment, not a temporary or symbolic gesture. Otherwise, not only will society fail to benefit, but the foundation of business sustainability itself will be undermined.
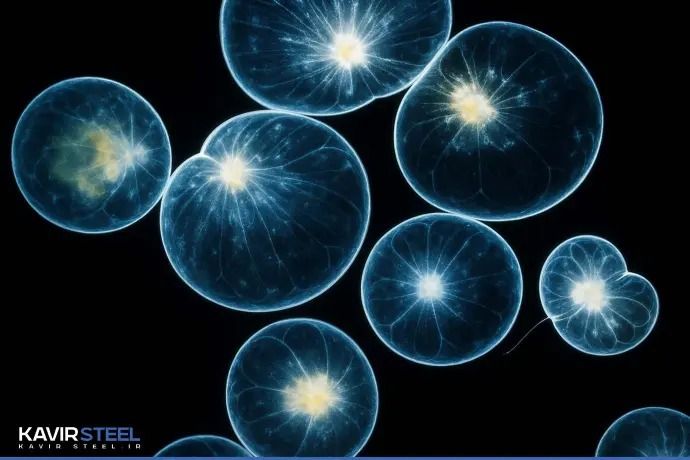
Bioluminescent Bacteria for Wastewater Toxicity Detection at Kavir Steel
Pioneering Use of Biotechnology in Iran’s Steel Industry:Bioluminescent Bacteria for Wastewater Toxicity Detection at Kavir Steel
The Kavir Steel processing plant is one of the most advanced industrial units in the field of wastewater treatment in Iran, designed and commissioned to provide a sustainable water supply for the company’s production lines. Using modern technologies, this facility converts municipal wastewater into high-quality water suitable for industrial processes, eliminating the need for groundwater extraction.
One of the standout features of this plant is its toxicity-detection system installed at the wastewater intake point where Kashan’s municipal sewage connects to the facility. This system utilizes biotechnology and bioluminescent bacteria to continuously and instantly monitor the quality of incoming wastewater.
The mechanism of this system is based on the biological response of these bacteria. Under normal conditions, bioluminescent bacteria produce an enzyme called luciferase, which enables them to emit light. When the incoming water is free from toxic substances, the bacterial light remains stable. However, when heavy metals or unusual pollutants such as blood, chemical waste, or industrial residues are present, the bacteria’s metabolism is disrupted and their light is extinguished. This loss of luminosity acts as a biological warning signal, prompting the system to alter the wastewater flow and prevent contaminated influent from entering the downstream treatment stages.
This protective system not only shields the active microorganisms essential to the treatment process from harm, but also ensures that no incompatible substances reach the plant, as the facility is engineered specifically for processing wastewater—and the introduction of any foreign elements could impair its performance.
The use of this technology reflects Kavir Steel’s broader strategy toward sustainable development, resource management, and innovation within the steel industry.
Advanced Material Handling System: The Backbone of Raw Material Supply at Kavir Steel
Another Step Toward Smart Manufacturing AchievedAdvanced Material Handling System: The Backbone of Raw Material Supply at Kavir Steel
In line with its mission to produce diverse and high-quality steel grades, Kavir Steel has taken a significant step forward by implementing an advanced process known as the Material Handling System (MHS). This system enables precise and targeted supply of raw materials to the steelmaking furnace.
The Executive Manager of the Kavir Steel Steelmaking Project explained the operational structure of this system:According to the finalized design, the steelmaking plant will benefit from full flexibility in raw material feeding, allowing production using either 100% direct reduced iron (DRI) or 100% scrap metal. In the initial stage of the process, DRI is transported via conveyor lines to dedicated storage silos. It is then transferred—through the material handling mechanism—to pre-allocated bins inside the production hall, and ultimately fed into the injection systems of the furnace equipment.
Amir Sadeghi elaborated on the raw material segregation stage:Metal scrap, as the other primary raw material, is collected in the scrapyard, where it is sorted and classified using mechanized equipment and physical/chemical identification methods. Criteria such as alloy composition, appearance, impurity level, and production purpose determine its categorization, after which it is placed in designated temporary storage zones. This structure enables the MHS to select and deliver the exact charge required by the furnace according to the target steel grade.
He added:The flexibility of the MHS allows the plant to rapidly switch between different grades and supply a tailored, optimized charge for every production order. This capability elevates the role of the MHS from a mere transportation system to a critical link in the chain of quality control and product diversification.
By deploying this smart and advanced system in its steelmaking project, Kavir Steel is establishing a robust foundation for the targeted and planned production of special-grade steels for industrial, construction, and medical applications. This milestone marks a decisive step toward industrial self-sufficiency and meeting the diverse demands of domestic and export markets.
Gallery
Show MoreVideo
Show MoreThe annual ordinary general meeting of the shareholders of Foulad Kavir was held
The annual ordinary general meeting of the shareholders of Foulad Kavir was held